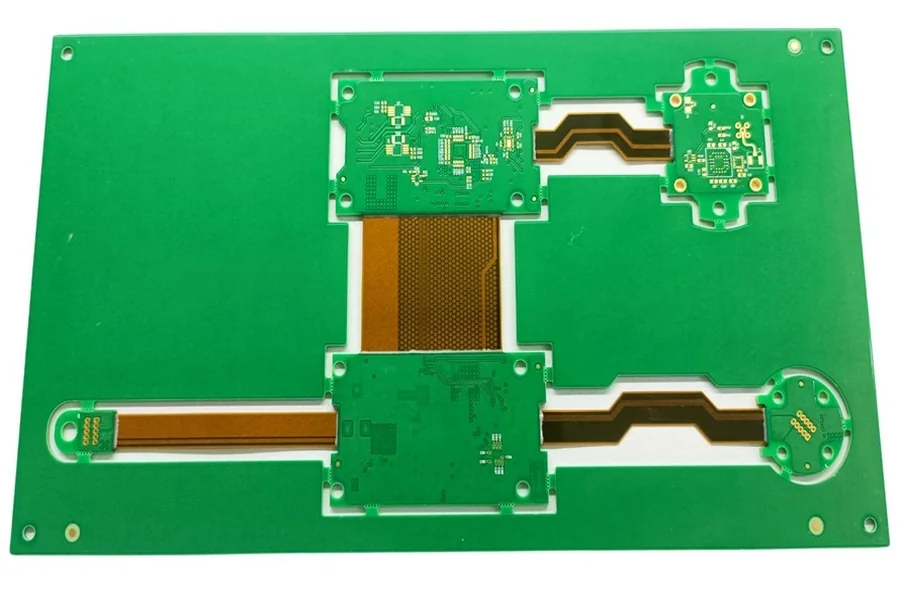
A rigid flex printed circuit board is a specialized type of PCB that combines the structural stability of a rigid board with the adaptability of a flexible board. This combination allows engineers to create circuits that can handle both mechanical stress and complex spatial layouts while maintaining excellent electrical performance. Instead of using separate rigid and flexible boards connected by cables or connectors, the rigid flex design integrates them into a single, unified structure. This not only saves space but also improves reliability by reducing the number of potential failure points.
Structure of a Rigid Flex Printed Circuit Board
The structure of a rigid flex printed circuit board is carefully engineered to deliver both flexibility and strength where needed. Rigid sections, typically made from FR4 or other fiberglass-reinforced epoxy laminates, provide a stable platform for mounting components. Flexible sections, usually made from polyimide film, allow the circuit to bend and fit into tight or irregular spaces. Copper layers run continuously between the rigid and flexible parts, ensuring uninterrupted electrical connections. These boards can be single-sided, double-sided, or multi-layered, depending on the design complexity and application requirements. The integration of rigid and flexible layers is achieved through precise lamination techniques that bond the materials together into one cohesive board.
Advantages of Rigid Flex Printed Circuit Board
One of the primary advantages of a rigid flex printed circuit board is its space efficiency. By allowing the circuit to fold or bend, designers can create compact electronic assemblies that would be impossible with traditional rigid boards. This makes them ideal for devices where space is at a premium, such as medical implants, aerospace controls, and portable electronics. Another major benefit is improved reliability. Eliminating separate connectors and cables reduces the chances of mechanical failure, signal loss, or interference. The durability of the rigid sections ensures that components remain securely mounted, while the flexibility of the bendable sections protects the board from stress caused by movement or vibration. Additionally, these boards can simplify assembly, reduce weight, and enhance thermal performance in demanding applications.
Manufacturing Process of Rigid Flex Printed Circuit Board
The manufacturing of a rigid flex printed circuit board requires advanced fabrication methods and precise control over materials. The process begins with the preparation of rigid and flexible substrates, which are cleaned and treated to ensure proper adhesion. Copper foil is laminated onto both rigid and flexible layers, and the circuit pattern is transferred through photolithography. The unwanted copper is etched away, leaving only the desired traces and pads. For multi-layer boards, additional layers are stacked and bonded using specialized lamination processes that preserve the flexibility of the bendable sections. Holes for vias and component leads are drilled or laser-cut, then plated to create conductive pathways between layers. Protective coatings, such as solder masks for rigid sections and coverlays for flexible sections, are applied before the board undergoes rigorous electrical and mechanical testing.
Applications of Rigid Flex Printed Circuit Board
Rigid flex printed circuit boards are used in a wide range of industries that require compact designs, high reliability, and the ability to operate in harsh conditions. In consumer electronics, they are found in foldable smartphones, wearable devices, and high-end cameras. The aerospace and defense sectors use them in avionics, navigation systems, and communication devices where weight savings and durability are critical. Medical applications include surgical instruments, diagnostic equipment, and implantable devices that must fit within extremely small enclosures while maintaining dependable performance. In the automotive industry, rigid flex PCBs are used in infotainment systems, advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), and various control modules that experience constant vibration and temperature fluctuations.
Advancements in Rigid Flex Printed Circuit Board Technology
Advancements in materials and manufacturing processes have expanded the possibilities for rigid flex printed circuit boards. New polyimide films with higher temperature resistance and improved mechanical properties allow for greater durability and more complex folding patterns. High-density interconnect (HDI) technology now enables more components to be placed in smaller areas, making these boards suitable for next-generation electronics. Laser drilling techniques allow for precise microvias, enhancing signal integrity and reducing electrical losses. These innovations have positioned rigid flex PCBs as a go-to solution for high-performance devices in cutting-edge industries, including 5G communications, space exploration, and advanced robotics.
Handling and Maintenance of Rigid Flex Printed Circuit Board
While rigid flex printed circuit boards are built to withstand challenging environments, they still require careful handling during assembly and maintenance. Excessive bending beyond the recommended radius can damage the copper traces or weaken the flexible substrate. Proper strain relief should be incorporated into the design to reduce mechanical stress on the bend areas. During soldering, controlled temperatures must be maintained to prevent heat damage, especially to the flexible sections. Anti-static precautions should also be observed to protect sensitive components from electrostatic discharge. Following best practices in handling and storage can greatly extend the lifespan and performance of a rigid flex PCB.
Future of Rigid Flex Printed Circuit Board in Electronics
The future of the rigid flex printed circuit board is closely tied to the growth of advanced electronics that demand compact size, reduced weight, and high durability. As devices become more interconnected and portable, the need for hybrid PCB solutions will continue to grow. From wearable health monitors to unmanned aerial vehicles, the versatility and reliability of rigid flex designs will play a key role in innovation. With further advancements in material science, manufacturing automation, and cost efficiency, rigid flex PCBs will likely see wider adoption in both high-end industrial systems and mass-market consumer products.
Choosing the Right Rigid Flex PCB Manufacturer
Selecting the right rigid flex PCB manufacturer is essential for ensuring that your project meets the highest standards of quality, performance, and reliability. An experienced manufacturer will have the technical expertise, advanced production capabilities, and rigorous quality control processes needed to produce boards that meet your exact specifications. They will also be able to guide you on design optimization, material selection, and cost-effective production methods. By partnering with the right manufacturer, you can achieve a product that performs flawlessly in its intended application while meeting project deadlines and budget requirements.