Using redshift security is quick, flexible, and provides security without a great deal of foundation knowledge. Furthermore, the Redshift security platform includes a number of information analysis tools, consistency tools, and, amusingly, AI and reasoning applications.
Data centers with conventional security differ in some basic ways from Redshifts. Learn five things that make redshift security different from others, as well as how you can make use of these features to make redshift security information useful.
Redshift’s Five Most Important Features
A very impressive cloud information distribution center, despite its commitment to constant growth, is stage’s design. The purpose of this post is to highlight the five essentials of redshift security engineering that make it unique.
● Discrimination Against Certain Groups
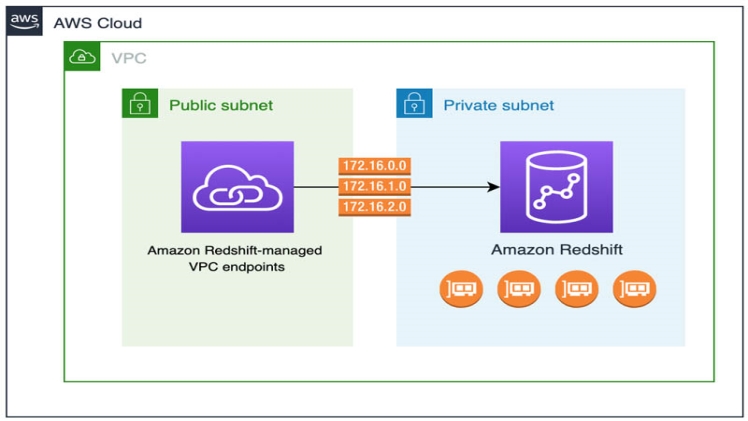
The organization can separate its users by identity if it requires extra security. VPCs restrict network access to cluster(s) in associations. IPsec VPN stays tethered to the client’s warehouse.
● Data Sets Based On Segmentation
Coordinating information over lines and sections is possible. A strategy’s type depends on its responsibility. Information is most commonly arranged by column. The reason is that systems placed along lines are fast at handling small tasks. To prepare data exchanges, OLTP, or online data processing, is a common method.
The segmented format is better for providing access to large data sets. As an example, OLAP or online insight preparation takes the form of clients presenting a few questions to large data sets. Because redshift security stores data in segments, it can process lots of data quickly.
● The Mutual Protection Protocol (MPP)
MPP uses a distributed configuration method to separate and win
a vast amount of information. The result of combining a large handling position with a smaller one is then divided among several larger processors (regular hubs). Parallel calculations are more efficient than sequential calculations. Redshift security can now handle one huge task in very little time.
● Defining Simultaneously
During concurrent processing, a client can arrange a maximum amount of hubs or bunches. All clients have access to a satisfying figure asset as a result of these cut-off points. This means that simultaneous arrival at the info center will limit its accessibility.
With Redshift security, multiple digital distribution networks run simultaneously at a point where they can be adaptable.
However, at the same time, they can handle the simultaneousness of information distribution. Bundles have a lot of hubs available to them based on the type of hub they have. Similarly, Redshift Security sets individual thresholds based on the area rather than imposing a single threshold. Occasionally, clients may request a cut-off for increments.
● Reconfiguring The System To Adapt To Internal Problems
It is the capability of a framework to adapt to failure that enables it to carry on even if some parts fail. When it comes to warehouse capacity, internal faults are decisive. Several unconnected computers prevent something crucial from running.
The information must be open and reliable for a client. Each group undergoes continuous screening. In the event of a failure of a drive, hub, or group, the redshift security system sequentially repeats information onto solid hubs.